
Easier access to scientific data

Brought to you by EMODnet Physics
 |
EMODnet Physics ERDDAP
Easier access to scientific data |
log in|
Brought to you by EMODnet Physics |

| Dataset Title: | EMODnet Physics - TEMPERATURE ANOMALY 10 YEARS

|
| Institution: | EMODnet Physics (Dataset ID: ERD_EP_TEMP_ANO_10Y) |
| Information: | Summary  | License
| License  | FGDC
| ISO 19115
| Metadata
| Background
| FGDC
| ISO 19115
| Metadata
| Background | Data Access Form
| Files
| Data Access Form
| Files
|
Click on the map to specify a new center point.

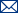
Zoom: ![[The graph you specified. Please be patient.]](https://erddap.emodnet-physics.eu/erddap/griddap/ERD_EP_TEMP_ANO_10Y.png?ANOMALY%5B(2019-06-30T00:00:00Z)%5D%5B(2.0102019E7)%5D%5B(-77.0104751586914):(89.8962631225586)%5D%5B(-180.0):(179.5)%5D&.draw=surface&.vars=longitude%7Clatitude%7CANOMALY&.colorBar=%7C%7C%7C%7C%7C&.bgColor=0xffccccff)
|
Attributes {
time {
String _CoordinateAxisType "Time";
Float64 actual_range 6.46704e+8, 1.5618528e+9;
String axis "T";
String ioos_category "Time";
String long_name "Time";
String standard_name "time";
String time_origin "01-JAN-1970 00:00:00";
String units "seconds since 1970-01-01T00:00:00Z";
}
depth {
String _CoordinateAxisType "Height";
String _CoordinateZisPositive "down";
Int32 actual_range 19901999, 20102019;
String axis "Z";
String ioos_category "Location";
String long_name "Depth";
String positive "down";
String standard_name "depth";
String units "m";
}
latitude {
String _CoordinateAxisType "Lat";
Float64 actual_range -77.0104751586914, 89.8962631225586;
String axis "Y";
String ioos_category "Location";
String long_name "Latitude";
String standard_name "latitude";
String units "degrees_north";
}
longitude {
String _CoordinateAxisType "Lon";
Float64 actual_range -180.0, 179.5;
String axis "X";
String ioos_category "Location";
String long_name "Longitude";
String standard_name "longitude";
String units "degrees_east";
}
ANOMALY {
Float64 colorBarMaximum 10.0;
Float64 colorBarMinimum -10.0;
String ep_parameter_group "Water Temperature";
String long_name "ANOMALY";
String units "degree_Celsius";
}
NC_GLOBAL {
String cdm_data_type "Grid";
String Conventions "COARDS, CF-1.6, ACDD-1.3";
Float64 Easternmost_Easting 179.5;
Float64 geospatial_lat_max 89.8962631225586;
Float64 geospatial_lat_min -77.0104751586914;
String geospatial_lat_units "degrees_north";
Float64 geospatial_lon_max 179.5;
Float64 geospatial_lon_min -180.0;
Float64 geospatial_lon_resolution 0.5;
String geospatial_lon_units "degrees_east";
String history
"2024-07-27T04:17:41Z (local files)
2024-07-27T04:17:41Z https://erddap.emodnet-physics.eu/griddap/ERD_EP_TEMP_ANO_10Y.das";
String infoUrl "https://portal.emodnet-physics.eu/";
String institution "EMODnet Physics";
String keywords "anomaly, data, latitude, local, longitude, source, time";
String license "Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike http://www.opendefinition.org/licenses/cc-by-sa";
Float64 Northernmost_Northing 89.8962631225586;
String sourceUrl "(local files)";
Float64 Southernmost_Northing -77.0104751586914;
String standard_name_vocabulary "CF Standard Name Table v29";
String summary "Data from a local source.";
String time_coverage_end "2019-06-30T00:00:00Z";
String time_coverage_start "1990-06-30T00:00:00Z";
String title "EMODnet Physics - TEMPERATURE ANOMALY 10 YEARS";
Float64 Westernmost_Easting -180.0;
}
}
 Data Access Protocol (DAP)
Data Access Protocol (DAP) and its
projection constraints
and its
projection constraints .
.
The URL specifies what you want: the dataset, a description of the graph or the subset of the data, and the file type for the response.
griddap request URLs must be in the form
https://coastwatch.pfeg.noaa.gov/erddap/griddap/datasetID.fileType{?query}
For example,
https://coastwatch.pfeg.noaa.gov/erddap/griddap/jplMURSST41.htmlTable?analysed_sst[(2002-06-01T09:00:00Z)][(-89.99):1000:(89.99)][(-179.99):1000:(180.0)]
Thus, the query is often a data variable name (e.g., analysed_sst),
followed by [(start):stride:(stop)]
(or a shorter variation of that) for each of the variable's dimensions
(for example, [time][latitude][longitude]).
For details, see the griddap Documentation.